[section label=1. Introduction]
TLC for the Datacenter
 A little less than two years ago, Samsung surprised the storage industry by unveiling the world’s first 3-bit MLC, or TLC (Triple Level Cell), NAND based SSD, the Samsung 840. At the time, TLC NAND had already been in use for storage applications such as flash drives and embedded systems, but nobody really thought TLC was viable for SSDs due to TLC’s inherently higher latency and its lower endurance compared to older MLC and SLC technologies.
A little less than two years ago, Samsung surprised the storage industry by unveiling the world’s first 3-bit MLC, or TLC (Triple Level Cell), NAND based SSD, the Samsung 840. At the time, TLC NAND had already been in use for storage applications such as flash drives and embedded systems, but nobody really thought TLC was viable for SSDs due to TLC’s inherently higher latency and its lower endurance compared to older MLC and SLC technologies.
Despite this, Samsung is now standing behind two generations of TLC based SSDs, proving a number of our initial preconceptions of TLC incorrect – the biggest of which is drive endurance. Unlike cMLC (consumer MLC) which is generally rated at ~3,000 P/E (Program/Erase) cycles, TLC is rated at an estimated ~1,000 – 1,500 P/E cycles (the actual number hasn’t really been revealed by Samsung). While it’s easy to base assumptions of an SSD’s endurance on the NAND’s P/E cycles, this is actually a very bad measure of a SSD’s total endurance. Endurance also depends on a SSD controller’s write algorithms, write amplification, garbage collection routines, and over-provisioning which is why Samsung is capable of claiming that their TLC based 840 SSDs can do 10GB/day and has “…no workload restrictions…” on their 3 year warranty as well.
Now that Samsung has proven TLC NAND on the client side, Samsung is now the first SSD manufacturer to take the same technology to the enterprise with a datacenter oriented derivative of their Samsung 840 EVO they’d creatively like to call the Samsung 845DC EVO.
Samsung 845DC EVO Specifications
| Manufacturer | Samsung | Samsung | Samsung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 845DC EVO | 845DC EVO | 845DC EVO |
| Form Factor | 2.5″ 7mm SATA | 2.5″ 7mm SATA | 2.5″ 7mm SATA |
| Capacity | 240 GB | 480 GB | 960 GB |
| Controller | Samsung MEX | Samsung MEX | Samsung MEX |
| NAND | 19nm Toggle Mode 3-bit MLC NAND | 19nm Toggle Mode 3-bit MLC NAND | 19nm Toggle Mode 3-bit MLC NAND |
| Sequential Reads | 530 MB/s | 530 MB/s | 530 MB/s |
| Sequential Writes | 270 MB/s | 410 MB/s | 410 MB/s |
| 4K Random Read | 87,000 IOPS | 87,000 IOPS | 87,000 IOPS |
| 4K Random Write | 12,000 IOPS | 14,000 IOPS | 14,000 IOPS |
| Interface | SATA 6GB/s | SATA 6GB/s | SATA 6GB/s |
| Warranty | 5 Years, 150 TBW | 5 Years, 300 TBW | 5 Years, 600 TBW |
The Samsung 845DC EVO will come in three capacities – 240GB, 480GB, and 960GB with all three drives available in the 2.5″ 7mm form factor. Similar to Samsung’s consumer grade 840 and 840 EVO, the Samsung 845DC EVO will receive overprovisioning out of the box to help improve both drive endurance and drive performance. Like many drives on the market, the Samsung 845DC EVO will receive ~7% overprovisioning, which is ~3-4% more overprovisioning than its consumer oriented cousins.
As it’s an enterprise grade drive, the Samsung 845DC EVO will receive a 5 year, variable TBW (Total Bytes Written) warranty based on capacity. The 240GB Samsung 845DC EVO is rated at 150 TBW while the 480GB version is rated at 300 TBW and the 600GB version is rated at 600 TBW.
Probably the biggest feature that separates the Samsung 845DC EVO from its consumer oriented cousins is that the 845DC EVO will also receive full data path power loss protection. This will allow the drive to flush the contents of its DRAM cache and any data in flight into non-volatile NAND in the event of sudden power loss to ensure 100% data integrity. This is a feature that’s required for many enterprise server deployments.
Let’s take a closer look at the Samsung 845DC EVO.
[section label=2. A Closer Look]
A Closer Look at the Samsung 845DC EVO
As true to an enterprise SSD, the Samsung 845DC EVO arrived in a small, non-descript brown box.
Inside the package, we simply get the Samsung 845DC EVO itself. The design of the Samsung 845DC EVO is fairly similar to the rest of Samsung’s SSDs except with a different color scheme. The casing appears to be the same metal shell carried over from the Samsung 840/840 EVO/840 PRO.
Cracking open the casing, we get a full sized PCB for both the 240GB and 960GB versions. This is slightly different from the consumer SSDs which had full size, half size and even quarter sized PCBs based on capacity.
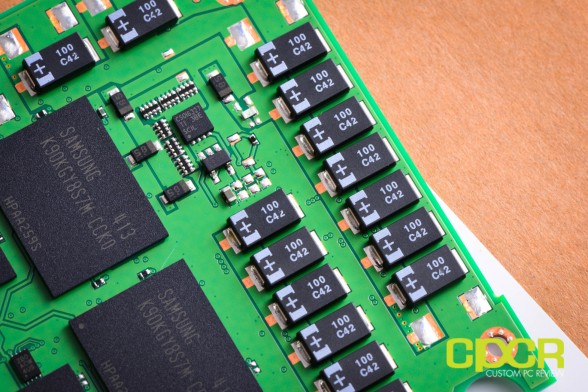
Powering the Samsung 845DC EVO is Samsung’s in-house tri-core MEX controller carried over from the Samsung 840 EVO which was introduced last year. This is an 8-channel controller with an internal clock frequency of 400MHz, 100MHz faster than the MDX controller used on the Samsung 840 PRO. Samsung hasn’t really released much additional details on the controller at this time.
For NAND, Samsung is using their in-house 19nm TLC (3-bit per cell MLC) Toggle NAND – pretty much the same stuff used in the Samsung 840 EVO. Aside from some in-house binning, I doubt Samsung has significantly changed the NAND between the 840 EVO and the 845DC EVO. The Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB edition includes a total of 256GiB of raw NAND capacity while the 960GB version includes a total of 1024GiB of raw NAND capacity. The Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB includes 4 NAND packages while the 960GB edition includes 8.
Onboard we also get a 1GB Samsung LPDDR2 512MB DRAM buffer chip for the onboard cache.
In addition to the enterprise oriented firmware and more robust warranty, the biggest feature differentiating the Samsung 845DC EVO from its client oriented counterparts is this array of Tantalum capacitors designed to protect data in flight and data in the DRAM cache in the event of sudden power loss.
[section label=3. Test Setup/Drive Information]
Haswell Test Bench
| System | CyberPowerPC Gamer Xtreme 4200 |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Core i7 4770K |
| Motherboard | ASUS Z87-A |
| Memory | Kingston HyperX Genesis 16GB DDR3 2133MHz |
| Graphics | Intel HD4600 Graphics |
| Storage | OCZ Vertex 4 256GB |
| Power Supply | Corsair HX650 |
| Case | HSPC High Speed Tech Station |
| Optical Drive | ASUS OEM DVD Drive |
| Operating System | Windows 8 64 bit & CentOS 6.4 |
Special thanks to CyberPowerPC, Kingston, OCZ Technology and HSPC for sponsoring our test bench!
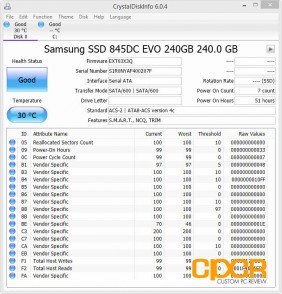
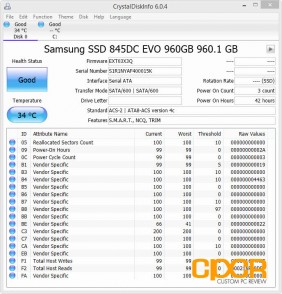
Crystal Disk Info
Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB, 960GB
Today we’ll be reviewing both the Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB and 960GB SSDs with firmware EXT03X3Q.
[section label=4. 4K Random Read/Write Performance]
Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB, 960GB Performance
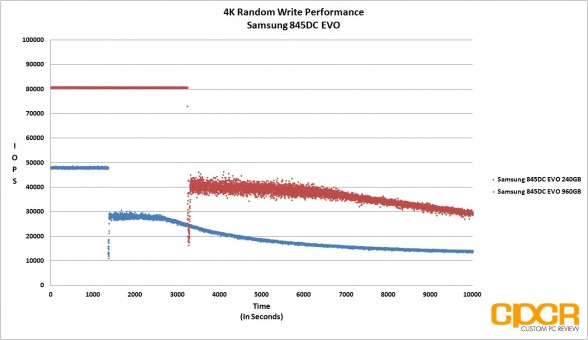
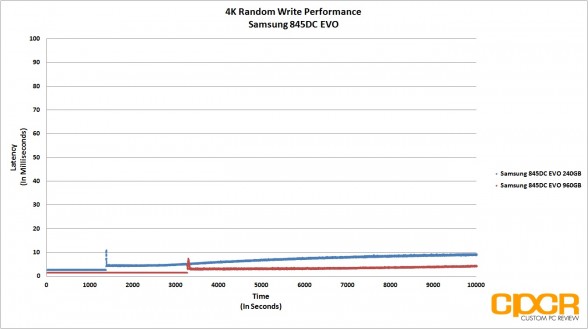
4K Random Write Preconditioning
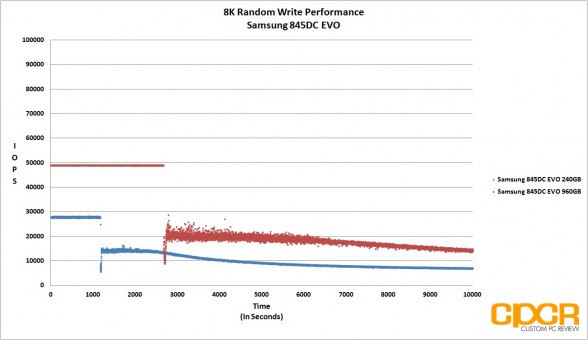
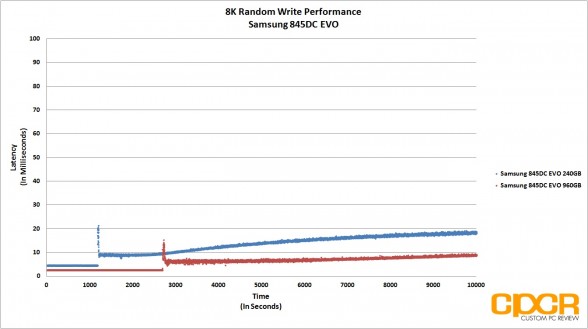
Before our 4K Random Read/Write performance testing, we’ll first precondition our enterprise SSD by secure erasing the drive then hammering it with a little over 10,000 seconds worth of 4K random writes at QD32. By recording the IOPS and latency every second during our run, it’s easy to see what kind of write performance can be expected as our SSD transitions from its fresh out of the box state into steady state.
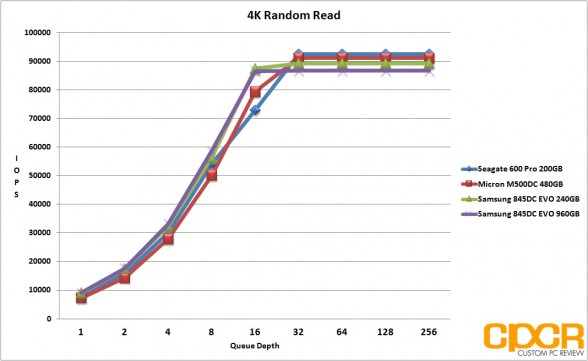
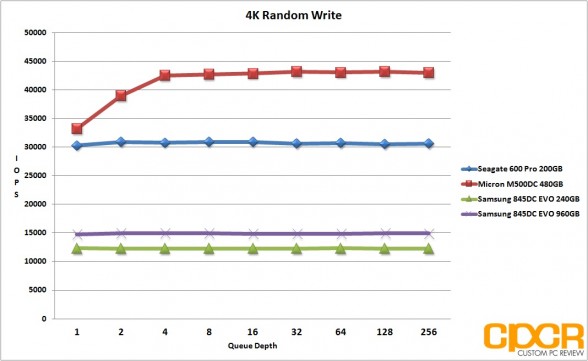
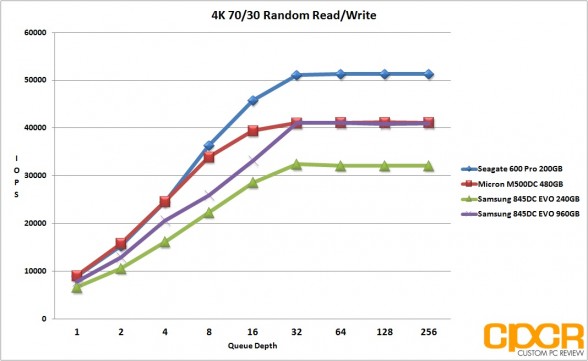
4K Random Read/Write Performance
After our 4K random write preconditioning, we then run two more passes of 4K random data through the enterprise SSD for consistency before conducting our actual testing below.
Performance Analysis
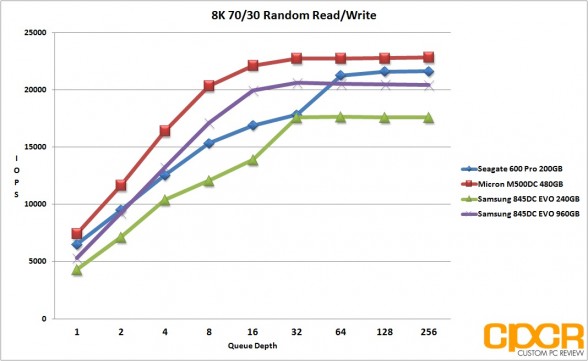
Looking at our results, the Samsung 845DC EVO is quite obviously heavily optimized for read workloads with both 240GB and 960GB capacities topping out at the rated 87,000 IOPS in 4K random reads, and 4K random write performance topping out at ~14,000 IOPS for the 960GB version and ~12,000 IOPS for the 240GB version. That said, the Samsung 845DC EVO 960GB version did very well in our mixed workload testing, matching the MLC based Micron M500DC 480GB at ~41,000 IOPS at higher queue depths.
Latency wasn’t an issue with both drives managing to keep things well under 20ms, even under heavy load.
[section label=5. 8K Random Read/Write Performance]
Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB, 960GB Performance
8K Random Write Preconditioning
Before our 8K Random Read/Write performance testing, we’ll first precondition our enterprise SSD by secure erasing the drive then hammering it with a little over 10,000 seconds worth of 8K random writes at QD32. By recording the IOPS and latency every second during our run, it’s easy to see what kind of write performance can be expected as our enterprise SSD transitions from fresh out of the box into steady state.
8K Random Read/Write Performance
After our 8K random write preconditioning, we then run two more passes of 4K random data through the enterprise SSD for consistency before conducting our actual testing below.
Performance Analysis
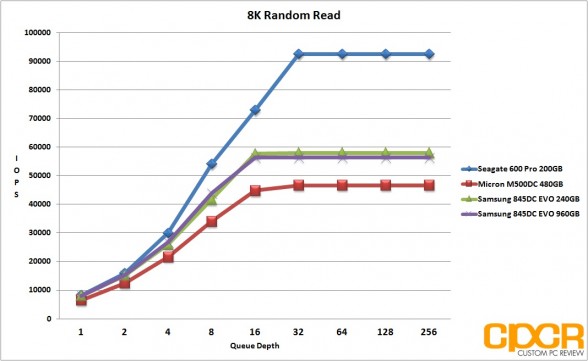
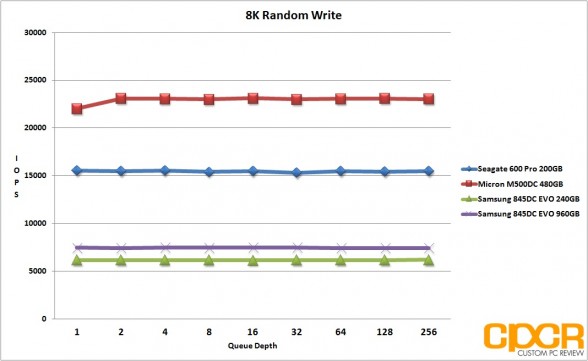
With 8K random workloads, the Samsung 845DC EVO once again excelled in read heavy workloads with both drives capable of pulling 57,000 IOPS 8K random reads. Random writes however, once again weren’t exactly the fastest out there with both drives struggling to pull past 8,000 IOPS. In a mixed workload environment, the Samsung 845DC EVO once again performed quite well with the drive pulling in at just under 21,000 IOPS.
[section label=6. 128K Random Read/Write Performance]
Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB, 960GB Performance
128K Random Write Preconditioning
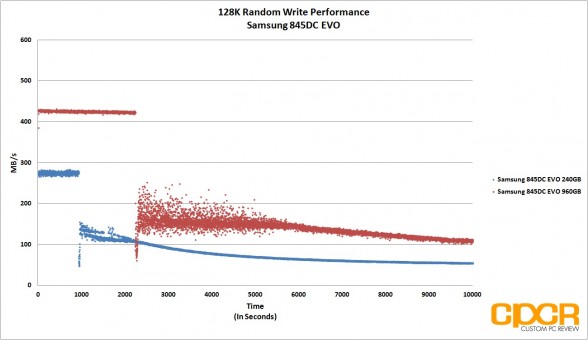
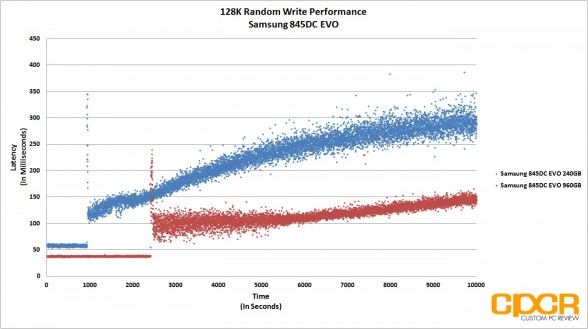
Before our 128K Random Read/Write performance testing, we’ll first precondition our enterprise SSD by secure erasing the drive then hammering it with a little over 10,000 seconds worth of 128K random writes at QD32. By recording the IOPS and latency every second during our run, it’s easy to see what kind of write performance can be expected as our enterprise SSD transitions from its fresh out of the box state into steady state.
128K Random Read/Write Performance
After our 128K random write preconditioning, we then run a two more passes of 4K random data through the enterprise SSD for consistency before conducting our actual testing below.
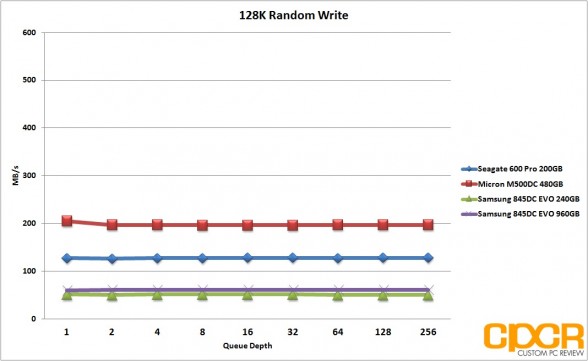
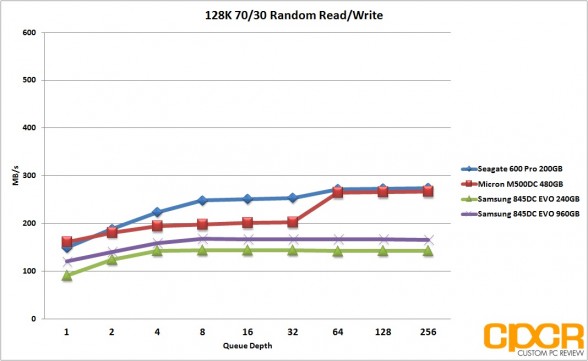
Performance Analysis
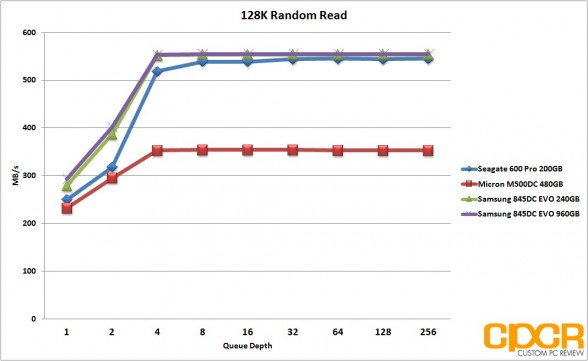
With 128K random reads, the Samsung 845DC EVO did extremely well with both the 240GB and 960GB capacity pulling a solid 554MB/s. Random writes unfortunately never got past 51MB/s for the 240GB capacity and 61MB/s for the 960GB capacity. Mixed workload performance was quite mediocre this time around as well as both drives struggled to pull past 170MB/s.
[section label=7. Server Access Patterns]
Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB, 960GB Performance
Server Access Patterns
While synthetic workloads are great indicators of a SSD’s performance, it’s not always indicative of how a SSD is actually going to be used in the real world. Very few applications for example will run continuous passes of 4K data at QD256. This is why we also run testing using typical access patterns users would face in the real world.
Testing here is conducted after a secure erase is performed followed by two full passes of 128K data followed by two full passes of 4K random data.
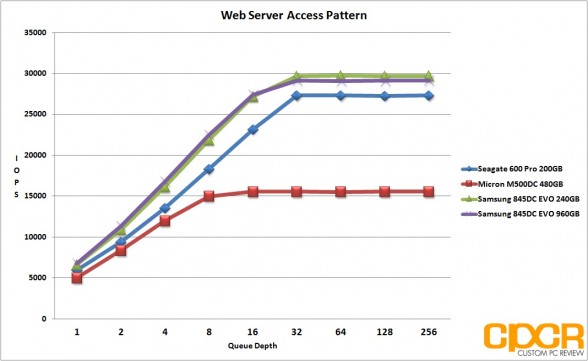
Web Server Access Pattern
Our web server access pattern simulates the type of activity found in a typical web server. The access pattern is made up of 100% reads with blocksizes ranging from 512b up to a maximum of 512K.
Access Pattern: 100% Read / 512b=22%, 1K=15%, 2K=8%, 4K=23%, 8K=15%, 16K=2%, 32K=6%, 64K=7%, 128K=1%, 512K=1%
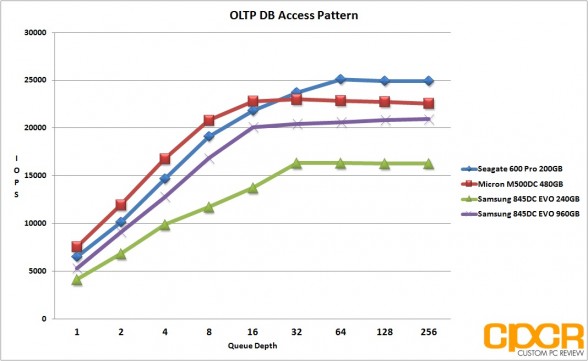
OLTP/Database Access Pattern
Our OLTP/Database access pattern simulates typical online transactional processing and database workloads. The access pattern here is made up to 67% reads and 33% writes at the 8K blocksize.
Access Pattern: 67% reads, 33% writes / 8K=100%
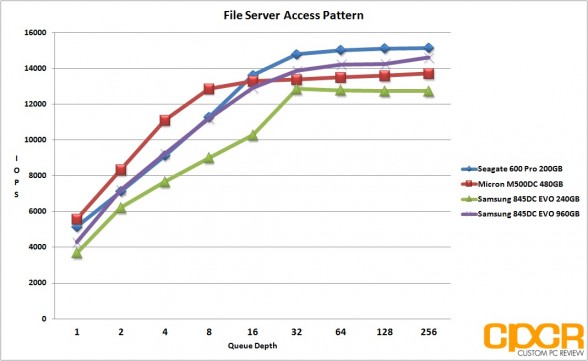
File Server Access Pattern
Our file server access pattern simulates a typical fileserver. The access pattern here is made up of 80% reads and 20% writes with blocksizes ranging between 512b to 64K.
Access Pattern: 80% reads, 20% writes / 512b=10%, 1K=5%, 2K=5%, 4K=60%, 8K=2%, 16K=4%, 32K=4%, 64K=10%
Performance Analysis
Since our server profiles are all read heavy, the Samsung 845DC EVO performed extremely well here, matching or beating competing MLC drives. While the 240GB version did suffer a bit in our OLTP database access pattern, the web server and file server access patterns looked extremely solid for both drives, especially the 960GB version which overtook the Micron M500DC in both tests.
[section label=8. Power Consumption]
Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB, 960GB Power Consumption
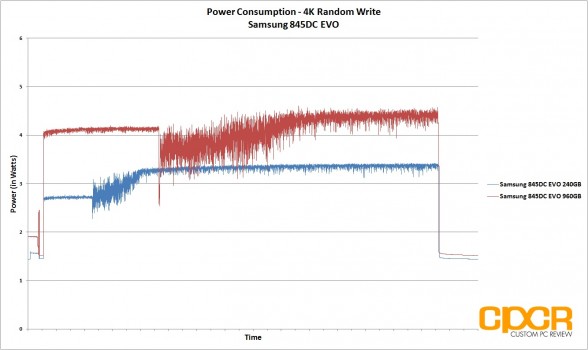
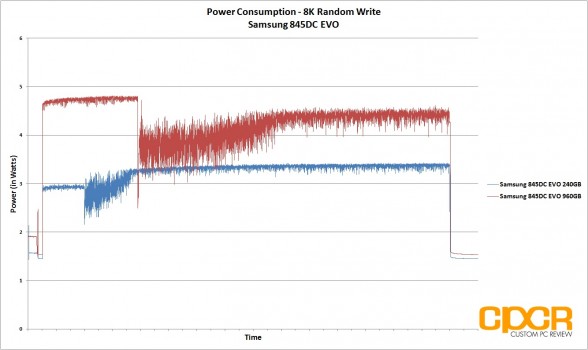
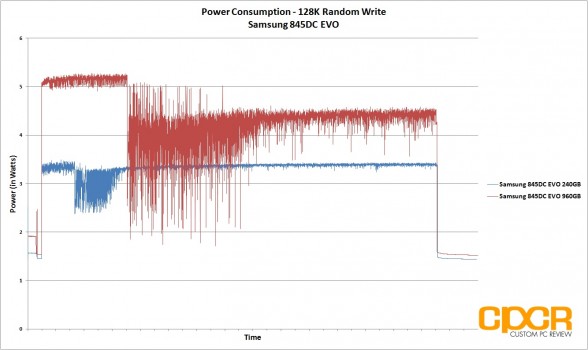
For our power consumption testing today, we’ll be conducting a trace on power draw during our 4K, 8K and 128K preconditioning runs. All power testing below is measured by tapping our calibrated B&K Precision 5491B Bench Multimeter directly into the 5v line running from the power supply to the drive.
Performance Analysis
Power consumption on the Samsung 845DC EVO was ~1.4w idle for the 240GB capacity and 1.5w for the 960GB capacity which is fairly similar for both capacities. That said, once the drives are under load, the 240GB capacity is significantly more power efficient, drawing a maximum 3.4w under load (128K random writes) compared to the 960GB capacity which drew 5.2w under load (128K random writes).
[section label=9. Conclusion]
Samsung 845DC EVO 240GB, 960GB Conclusions
 Unlike other SSD manufacturers who make significant modifications to differentiate their client and datacenter oriented products, Samsung tends to take a more simplistic approach – rather than developing a whole new product from the ground up specifically for the enterprise, simply take a proven client SSD and tune it for enterprise needs. This is exactly the approach taken for the Samsung 845DC EVO.
Unlike other SSD manufacturers who make significant modifications to differentiate their client and datacenter oriented products, Samsung tends to take a more simplistic approach – rather than developing a whole new product from the ground up specifically for the enterprise, simply take a proven client SSD and tune it for enterprise needs. This is exactly the approach taken for the Samsung 845DC EVO.
Performance wise, the Samsung 845DC EVO is quite good and it’s quite evident that Samsung built the drive to take advantage of the strengths of the NAND rather than try to focus on improving its weaknesses. Users looking for a drive for heavy, read intensive workloads will find the Samsung 845DC EVO probably the best low cost, entry level enterprise SSD on the market. Even users with small file, 80/20 read/write mix or a 70/30 read/write mix will probably want to take a deeper look into the Samsung 845DC EVO as well. Unfortunately, those looking for something to do more write intensive workloads or large block mixed workloads should probably look at alternatives – if not for better write performance, then for higher endurance ratings.
| Manufacturer | Samsung | Samsung | Samsung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 845DC EVO | 845DC EVO | 845DC EVO |
| Capacity | 240 GB | 480 GB | 960 GB |
| Street Price | $249.99 | $489.99 | $969.99 |
| Price/GB | $1.04 | $1.02 | $1.01 |
| Check Pricing | Click Here | Click Here | Click Here |
Pricing on the Samsung 845DC EVO is currently ~249.99 for the 240GB model, $489.99 for the 480GB model and $969.99 for the 960GB model at various e-tailers which translates to around $1.01-$1.04/GB. For an enterprise datacenter oriented drive, the Samsung 845DC EVO is very price competitive considering competing products such as the Micron’s M500DC retails at ~$1.21/GB and Intel’s DC S3500 retails at ~$1.28/GB. That said, Samsung’s enterprise division’s interest is primarily in large volume sales (10,000+ units) to their partners/OEMs rather than selling in retail, so pricing will be different depending on quantity ordered.
While inexpensive compared to the competition, I still think the Samsung has room to cut pricing on the 845DC EVO a bit further to be a bit more competitive especially since the design of the drive is really only a slightly reconfigured Samsung 840 EVO. Whereas something like Micron’s M500DC significantly differentiates itself from the consumer grade Crucial M500 with gobs and gobs of overprovisioning, a 1.9PB TBW warranty, and significantly improved write performance, Samsung hasn’t really done all that much with the 845DC EVO to command such a huge premium over their own consumer drive. Personally, I feel like hyperscale or cloud datacenters who want cheap drives for extremely read intensive workloads will end up using dirt cheap MLC consumer drives such as the Crucial M500 while those who want something for more write intensive workloads will go with higher endurance, higher write performance drives such as the Intel DC S3500/S3700 or Micron M500DC/P400m instead.
Ultimately, the Samsung 845DC EVO is a fantastic, cost effective enterprise SSD that’s extremely well suited for read-heavy workloads. Cost conscious datacenters currently looking into deploying consumer grade SSDs, yet still value the assurance of an enterprise grade warranty and power loss protection should seriously consider the Samsung 845DC EVO.
Sample provided by: Samsung
Available at: CDW